Views: 10 Author: Site Editor Publish Time: 2024-05-08 Origin: Site








Investment casting is a highly sophisticated and precise casting process used to cast complex metal parts. Investment casting plays a vital role in almost every industry, from aerospace, transportation (trains, cars, ships, etc.), kitchen and bathroom, mechanical equipment, pump and valve industry, tool and gage, military production, medical and jewelry.
However, achieving such precision requires strict quality control measures to ensure the integrity and reliability of the final product. In this article, we will delve into the world of investment casting and explore the various quality control techniques used to maintain high quality standards.
One of the main quality control measures in investment casting is raw material inspection (IQC).
The quality of the raw materials used directly affects the performance and durability of the final product. Therefore, meticulous inspection and testing of various raw materials is the first step in ensuring quality and is essential to identify any impurities or inconsistencies that may compromise the integrity of the casting. Spectroscopy and X-ray fluorescence are used to analyze the chemical composition of steel and alloys in the raw materials and verify that they meet the required specifications.
Another key aspect of quality control in investment casting is mold making.
High-quality molds can produce high-quality wax models, and are also a necessary condition for producing high-quality castings. To accurately place the shrinkage rate, the key step in manufacturing the mold is to design the mold structure reasonably. The requirements are that there are few parting surfaces, simple structure, easy operation, and the wax model is not easy to dent. The mold material is generally made of 7075 aluminum alloy, which is not easy to rust, has low density and high strength. In order to ensure the accuracy of the mold, computer-aided design (CAD) software can be used to design the mold.
After the mold is ready, the next step of quality control is the casting process itself:
use the mold to make a qualified wax model, which is almost the same as the final required casting (just the shrinkage rate and feed port are placed), and the parting line and feed port must be repaired and the wax model must be checked for deformation and dents.
The next step is to determine the number of groups, which is the most critical. It is best to discuss and decide with multiple technicians, because it is not only related to the shell making operation, wax removal, and cutting, but more importantly, it is related to the solidification method of the casting and the avoidance of shrinkage cavities and shrinkage.
The next step is to make a shell mold, immerse the wax mold in the surface slurry, pay attention to evenly apply the slurry to each position, sprinkle sand, and repeat this 5 or 6 times. Because silica sol is physically hardened, special attention should be paid to the temperature, humidity and wind speed control in the drying room; then dewax under heating and pressure, leaving a cavity.
Then pour the melted and qualified required metal liquid into the mold cavity. During this period, the pouring temperature, pouring speed and deoxidation should be controlled.
After cooling, the outer shell mold is cleaned, and the casting is cut off from the die head and polished to obtain the required casting.
After casting, quality control should continue, including inspection and testing of the finished casting.
Visual or vernier caliper inspection is carried out to identify any surface defects or dimensional deviations. For critical castings with relatively high requirements, non-destructive testing technologies such as X-rays or ultrasound must be used to detect internal defects that may not be visible to the naked eye. According to customer requirements, some mechanical property tests such as yield strength, tensile strength, hardness, impact test, air tightness test and salt spray test are also required to evaluate the mechanical properties of the casting and ensure that it meets the required standards.
In addition to these measures, quality control of investment casting also involves traceability and documentation. Each casting is assigned a unique identification number to facilitate tracking of relevant data of its manufacturing process. This traceability ensures accountability and facilitates any necessary investigation or recall. In addition, quality parameters, test results and certifications in the production process should be fully recorded to provide a transparent record that meets industry standards and customer requirements. Use the seven major quality control methods and PDCA cycle as much as possible to improve product quality every day, every month, and every year!
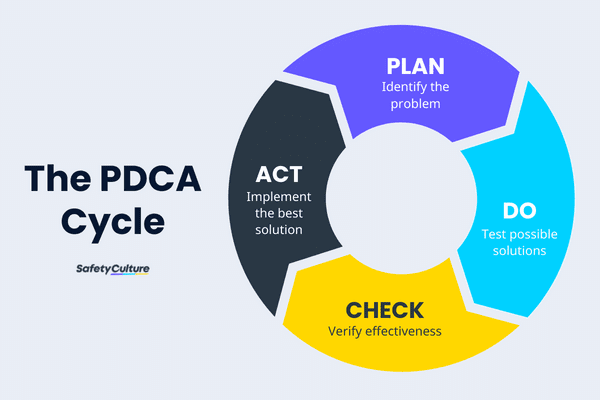
In short, the quality control measures of investment casting should be carried out throughout the entire production process, strictly implement self-inspection, mutual inspection and inspection of the next process on the previous process to ensure that the final product meets or even exceeds customer requirements. From the meticulous inspection of raw materials to the production of precision molds, the monitoring of casting parameters and the comprehensive inspection after casting, each step is carefully executed to minimize defects and maintain high standards. By complying with the above quality control measures, we can provide parts that meet the requirements of different industries and different customers, thereby winning the trust and satisfaction of customers.